Digestive Enzymes
Limited Edition Flavours

Digestive Enzymes
Description
Contents
- 1 What are Digestive Enzymes?
- 1.1 Protease
- 1.2 Amylase
- 1.3 Lactase
- 2 Digestive Enzyme benefits
- 2.1 Protease benefits
- 2.2 Amylase benefits
- 2.3 Lactase benefits
- 3 When to take Digestive Enzymes
- 4 How to take Digestive Enzymes Supplement
- 5 Gas and stomach bloating
- 6 Weight loss
- 7 Bodybuilding
- 8 Digestive Enzymes vs. Probiotics
- 9 Digestive Enzyme side effects
- 10 Supplement Facts
- 11 Warnings
- 12 Allergen warnings
- 13 References
What are Digestive Enzymes?
Digestive Enzymes are proteins secreted by the pancreas that help the body break down starch, fats and proteins to be converted into energy. Raw foods provide digestive enzymes but poor diet choices, stress, and fast eating can inhibit the effect of enzymes.[11] Digestive enzymes are produced in the pancreas, stomach, and salivary glands. In order for your body to manufacture enzymes, you need to eat trace minerals, which are found in raw foods. If your diet is deficient in raw foods, then you will also have an enzyme deficiency.[1] Furthermore, because of the quality of produce that is grown with pesticides in poor, nutrient deficient soil, genetically modified and at times frozen, it is difficult to find sufficient fruits and vegetables that are healthy to eat. Organic produce is the best way to go, but for those who cannot afford an organic, whole foods diet, ingesting a digestive enzymes supplement is an excellent option.
Protease
Protease is the enzyme responsible for breaking down proteins into amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of DNA, so their presence in the body system is vital. This enzyme is especially beneficial for athletes.
Amylase
Amylase breaks down carbohydrates into glucose that is processed by the body and used as energy. It is present in the saliva and begins working as soon as mastication begins. This enzyme can be used to aid in weight loss.
Lactase
Lactase breaks down lactose, a sugar in milk and milk by products such as cheese, pudding, etc. People who have a deficiency of lactase are said to be lactose intolerant.[13]
Digestive Enzyme Benefits
Digestive enzyme supplements are useful in improving overall body heath over time. Supplements with enzymes such as protease help with fat loss through breaking down fat stores.[12] To determine if a digestive supplement would be beneficial for you, ask yourself the following questions: Do you feel excessively full or bloated after meals? Does your food just sit in your stomach after eating? Do you suffer from constant gas or heartburn? Is there undigested food in your bowel? These are all symptoms of enzyme deficiency.[11] As mentioned above it is difficult to get all the enzymes the body needs from diet alone, much less the trace minerals that enzymes require in order to work properly. A healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, low on processed carbohydrates and including a regimen of digestive enzyme supplements aids with a number of ailments.
Protease benefits
The activity level to look for in protease is 40,000 HUT.[1] This enzyme is great in aiding the release of protein into the blood stream to assist with muscle recovery.
Amylase benefits
Amylase breaks down complex carbohydrates and starches. Once broken down they are converted into glucose that supplies the body with energy. Supplementing your diet with amylase is particularly important if you are a fast eater who does not chew enough. In a supplement, the activity level to look for is 16,000 SKB.[1]
Lactase benefits
Because milk is a major source of calcium, and people who do not get enough calcium in their diet can develop osteoporosis, a lactase supplement can be vital to good health by enabling a person to consume milk.[13] Vitamin D is another nutrient found in milk. Mothers who breastfeed have a special need to drink milk with Vitamin D to ensure their newborn gets enough of this nutrient. If the mother is lactose intolerant, an option for her is to take a lactase supplement. Symptoms of lactase deficiency include mild gas and bloating. Approximately 70% of people suffer from this while ignoring the symptoms. 1/3 of people in the United States are thought to be lactose intolerant. The activity level to look for in a supplement of lactase is 2,500 LACU.[1]
How and when should it be consumed
Health Canada Recommended Dose: Adults: 1 - 2 Capsule(s) 1 - 3 time(s) per day Take with or immediately before a meal/food.
Gas and stomach bloating
Digestive enzyme supplements, more specifically Lactase, can help treat gas and bloating in people who suffer from lactose intolerance. Gas, heartburn, constipation and other digestive issues can all be treated with a regimen of enzymes. These supplements aid in the digestion and emptying of the stomach faster, which relieves the above symptoms. "For common digestive complaints such as flatulence, bloating, heartburn, or irritable bowel syndrome: Take 1 to 2 capsules with smaller meals; 2 to 4 with large meals."[14]
Weight loss
Digestive enzymes can have a positive effect in a weight loss regimen. In order to lose weight, the state of waste system, stress, and organs all need to be taken into account. Protease is needed to help breakdown proteins and eliminate toxins. It is difficult to lose weight if the body is storing excess toxins. These toxins can cause an individual to feel more hungry, and then to eat more. It may take up to three weeks to see results as the enzymes do their job, eliminating toxins and aiding in digestion. Another three weeks are needed to see a complete renewal in energy.[7]
Amylase improves glycemic homeostasis, the balance of insulin and glucagon in the bloodstream after eating carbohydrates. This can aid in weight loss by inhibiting an excess of insulin, which causes weight gain. "Digestive enzymes really do something. They are not a placebo. They work quickly. In seconds, they break down the simple carbs."[1]
Bodybuilding
Bodybuilders need to consume a gram of protein per pound of bodyweight every day. However, if the protein consumed is not effectively broken down by the body, the individual is not maximizing their protein intake. Digestive enzymes containing protease help the body break down protein so it can be better absorbed.[10] Protease enzymes added to whey protein powder enable easier digestion and absorption of the whey. This allows more of the amino acids to enter the blood stream to be used by the muscles. Protease aids in the recovery of athletic injuries by speeding healing time and decreasing inflammation. A recent study showed that after 30 minutes on a treadmill, subjects who ingested protease supplements were able to maintain the fitness of their hamstrings better than subjects who did not take protease.[4]
Digestive Enzymes vs. Probiotics
Probiotics are bacterial organisms that live in our digestive system. The signs deficient healthy enzymes and probiotics in our bodies are similar, such as gas, bloating, constipation and heartburn. Enzymes are very sensitive to their environment, and heat can kill enzymes present in the food we eat. Temperatures as low as 100? can start to impact enzymes. Steroids, chlorinated water, refined sugars, and stress can denature natural levels of good bacteria.[9] In understanding the differences between specific enzymes and probiotics, confusion comes into play because many people confuse lactase with the probiotic L-Acidophilus, bacteria found in yogurt that is needed in your stomach for healthy digestion. Unlike enzymes, probiotics are living organisms with a life cycle of about a few months to even a few years. Both enzymes and probiotics benefit from trace minerals found in the body. Because minerals help activate enzymes it is important to eat a diet rich in raw vegetables and fruits. Like with enzymes, probiotics are found in foods but the amount needed by an individual may sometimes be difficult to attain through diet alone, and in that case, a supplement is recommended.[8]
Digestive Enzyme side effects
Because the body rapidly processes digestive enzymes, serious digestive enzyme side effects are not common. Use common sense guidelines when beginning a regimen for the first time, and if symptoms such as cramping, issues with bowel or sore stomach occur then adjust the dose. However, such symptoms usually resolve themselves in a few days. Any regimen designed to eliminate toxins from the body will cause discomfort during the first few days of the cleaning out process. However, if painful symptoms occur and do not subside, a doctor should be consulted. In addition, attempting to treat serious chronic conditions with digestive enzymes before consulting a doctor is not recommended.
The use of digestive enzymes in a healthy individual will help to correct ailments due to an imbalance in the body caused by poor diet and a sluggish system. Once toxins are eliminated and the natural working order of the body is reestablished, an individual on a regimen consisting of a good diet and digestive enzyme supplements will find his/herself returned to their full level of energy and able to enjoy their body in the best health possible.
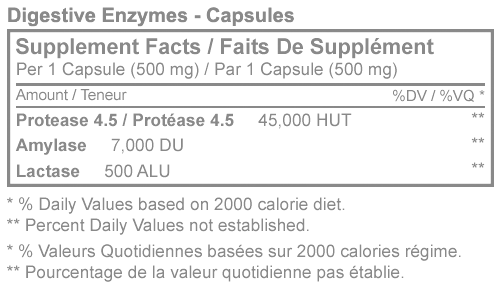
Supplement Facts
Warnings
Caution: Not intended for children, pregnant, or breastfeeding women. Consult a healthcare practitioner prior to use. Consult a healthcare practitioner prior to use if you have health conditions. Store in a cool dry place away from children. Do not use if seal is broken.
Allergen warnings
Allergy Statement: Manufactured in a facility that processes milk, soy, eggs, peanuts, wheat, tree nuts, sulphites, sesame and seafood.
Disclaimer: The above description does not constitute medical advice and is for informational purposes only and has not been evaluated by Health Canada, CFIA, or FDA. Please consult a properly licensed medical professional before consuming nutritional supplements. This product is not intended to treat, diagnose or cure any disease.
Suggested Use
Duration of Use
For prolonged use, consult a health care practitioner.
Recommended Dose
Adults: 1 - 2 Capsule(s) 1 - 3 time(s) per day
Take with or immediately before a meal/food.
Ingredients
Medicinal Ingredients (per dose unit): Protease 4.5 (Protease, Fungal protease, Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae - Whole) .......................... 45000 FCC hemoglobin units on the tyrosine basis (56.25 Milligrams) alpha-Amylase (4-alpha-D-Glucan glucanohydrolase, alpha-Amylase, Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae - Whole) .......................... 7000 FCC alpha-amylase dextrinizing units (46.67 Milligrams) Lactase (beta-galactosidase, Lactase, Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae - Whole) .......................... 5 Milligrams (500 FCC acid lactase units) Non-Medicinal Ingredients: Gelatin Brown rice flour
Nutrition Facts
Nutrition Facts
Serving Size 0
Servings Per Container
| Amount Per Serving | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calories 0 | ||
| % Daily Value* | ||
| Total Fat 0g | ||
| Saturated Fat 0g | ||
| Unsaturated Fat 0g | ||
| Trans Fat 0g | ||
| Cholesterol 0mg | ||
| Sodium 0mg | ||
| Total Carbohydrate 0g | ||
| Dietary Fiber 0g | ||
| Sugars 0g | ||
| Protein 0g | ||
* Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your calorie needs:





